Abdominal pain in early pregnancy: possible reasons
Abdominal pain in early pregnancy is quite a common phenomenon. The causes of this unpleasant pain can be very different. Some of them are harmless. Others are a serious threat to your pregnancy.

In some cases of sharp abdominal pain, it is very important to start treatment as soon as possible. Therefore, if you have any doubt, consult your gynecologist.
Physiological pain
Fortunately, in the absolute majority of cases, abdominal pain in early pregnancyis physiological. Such pain usually does not cause much inconvenience. It is almost imperceptible. In some cases, women feel pain not only in the abdominal, but also in the lower back.
The first pains can occur a week after conception — in the third week of pregnancy. During this short period, the fertilized egg embeds itself in the endometrium. Microscopic damage to the mucosa and blood vessels may cause pain and even slight bleeding.
In the first month of pregnancy, women feel pain in the abdomen because of hormonal changes. Increasing progesterone blood levels cause pain. In addition, since the fifth week of pregnancy some other body changes begin. Your ligaments are stretching and the center of gravity of your body is changing. All these can also cause pain in the lower abdomen.
Physiological pains in early pregnancy are completely harmless and do not require medical intervention. All the same, consult your doctor, as some more dangerous conditions have similar syndromes.
Pathological pain in early pregnancy
Unfortunately, sometimes abdominal pain in early pregnancy can be caused by more dangerous conditions.
- Intrauterine death
Sometimes, due to various reasons, the development of a fetus stops, and the fetus dies. A woman’s body rejects the dead fetus, causing contractions of the uterus, and, as a consequence, pronounced pain in the lower abdomen. In this case, the pain is sharp. It may also be bleeding.
Alas, nothing can be done. Doctors can only make sure that parts of the fetus do not remain in the uterus. If necessary, they’ll scrape the uterine lining.
- Ectopic pregnancy
In some cases, after getting to the uterus, a fertilized egg attaches to one of the fallopian tubes. Soon it reaches a size that exceeds the diameter of the tube, and a woman feels pain in the lower abdomen. Ectopic pregnancy is characterized by a large set of symptoms: pain localized in a particular place, profuse bleeding and severe pain if the tube is torn, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, fainting. If you have such symptoms, immediately consult a doctor. It’s not easy to restore the fallopian tube if it is torn.
Regardless of the fact, whether ectopic pregnancy was detected in time, a woman with this diagnosis is unlikely to avoid surgery. Only in extremely rare cases, when ectopic pregnancy was detected at a very early stage and the size of the ovum is very small, drugs for medical abortion can help.
- Threat of miscarriage
Abdominal pain in early pregnancy can indicate threatened miscarriage. This means the detachment of the ovum. Depending on how strong this detachment is, a woman has several symptoms:
- sharp pain in the lower abdomen;
- bleeding or spotting — from light pinkish to a rich red discharge.
A woman may have one of the symptoms or both.
If you have such symptoms, immediately call an ambulance. Then lie down and wait for the arrival of the doctor. Don’t panic. In most cases, timely treatment helps save the pregnancy. Don’t fuss! You can have a couple of tablets of Drotaverine (NO-SPA) for muscle relaxation.
- Corpus luteum cyst
Yellow body (Corpus luteum) is a temporary endocrine structure formed in the body of a woman to maintain her pregnancy. It develops on the site of a ruptured follicle. Yellow body produces progesterone during the first months of pregnancy until the placenta is completely formed.
In some cases, the development of Yellow body goes wrong. It accumulates fluid and becomes extremely big in dimensions — this is Corpus luteum cyst. This condition can cause abdominal pain but it is rarely dangerous for pregnancy.
Usually, pain from corpus luteum cyst is localized in a particular place and is not sharp. This pathology does not require intervention. There are some recommendations for women who are diagnosed with Corpus luteum cyst. They should avoid
- physical exercises,
- doing sports,
- long hikes,
- lifting heavy things,
All these may cause rupture of the cyst. In case of a rupture, the symptoms will be similar to those described in the section about ectopic pregnancy, because in both cases there is a profuse internal bleeding.
Non-gynecological reasons for abdominal pain
Pain in the abdomen in early pregnancy can be unrelated to gynecological reasons. Diseases such as cystitis, pyelonephritis, and appendicitis can cause pain. Each of them can occur in early pregnancy.
Lower abdominal pain in can be caused by bloating. In early pregnancy, gastrointestinal disorders are very frequent. In this case, I can only advise you to change your diet.
- Dyspeptic symptoms.
In early pregnancy, most powerful hormonal changes occur in a woman’s body. The process of adaptation to these changes may be a reason for abdominal pain. Even changing eating habits and plenty of salty or acidic foods in the diet can lead to permanent disruption of the digestive system, occurrence of flatulence and bouts of abdominal pain. The treatment of dyspeptic symptoms is carried out by using drugs that regulate the acidity of gastric juice or oppress the processes of gas formation in the intestine.
- Acute cystitis
Many pregnant women have decreased immunity. Uterus pressure on the bladder, wrong underwear, non-compliance of personal hygiene rules and hypothermia can cause cystitis. This inflammation causes sharp pain in the lower abdomen, which intensifies while urinating. A woman with acute cystitis feels frequent urge to urinate and sometimes has fever.
- Acute appendicitis.
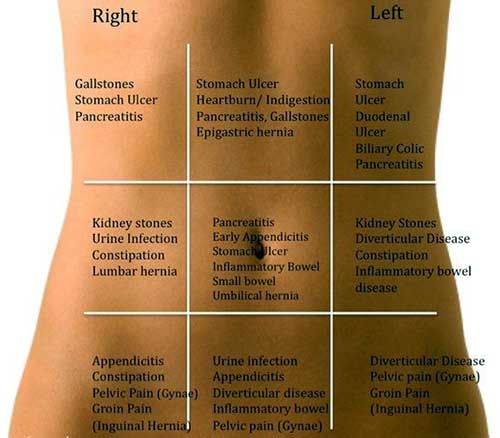
As any other person, a pregnant woman has a risk of inflammation of the vermiform appendix. During this disease, the pain occurs in the epigastrium, gradually moving to the right side. Other symptoms of intoxication can also be observed: fever, nausea and vomiting. Acute appendicitis must be treated in hospital.
- Acute or chronic cholecystitis.
Unhealthy diet and gallstones can trigger an attack of chronic or acute cholecystitis. In this case, pain is localized in the right upper quadrant, it is constant and drawing. Pain can aggravate after changing of body position. There are often nausea and vomiting. Pregnant women with this diagnosis are urgently hospitalized.
If you have abdominal pain in early pregnancy, you should not panic, it is better to calm down, and consult a doctor as soon as possible. If the pain is not sharp, there is no spotting and other unpleasant symptoms, you can come to his office, otherwise it is better to call an ambulance.