5 Signs of Hip Dysplasia in Babies
Hip dysplasia in newborns is the pathology of musculoskeletal system development, which forms in utero. It is underdevelopment of some structures and elements of a hip joint. This disorder usually means muscle weakness and excessive mobility of the femur.
This disease can provoke spine curvature, osteochondrosis, arthritis, subluxations and dislocations of the opposite joint, violations of the anatomy of the pelvis and hip bones. It is important to start treatment immediately after diagnosis because this pathology can lead to disability in adulthood.
Baby girls have hip dysplasia 4 times more often than boys do. In about 60% of cases, the pathology is in the left hip joint. In 20% of cases in the right joint, and in 20% in both hip joints.
Baby hip dysplasia is a very common congenital disorder that can be caused by many factors.Causes of Infant Hip Dysplasia.
- Heredity and predisposition.
In 25−30% of cases, dysplasia occurs in babies, whose parents suffered from this disorder in childhood or have diseases of the musculoskeletal system in adulthood. The gene that causes hip dysplasia is passed down the maternal line.
- Defects of embryonic development.
Violations in organs and tissues during fetal growth, which lead to hip dysplasia, often occur under the influence of negative environmental factors, infections or early toxemia of the mother, lack of vitamins or minerals during pregnancy. Dysplasia of the hip joints can form because of the limited mobility of the baby in the womb. It is most often in premature infants.
- Hormonal causes.
Excessive production of female sex hormone progesterone in the last weeks of pregnancy causes muscular weakness. 30−40% of all dysplasia cases are because of this reason. After birth, hormonal influence stops and dysplasia disappears in 1−2 months without any treatment.
- Malformations of the whole musculoskeletal system.
What happens with a hip joint?
The normal development of a hip joint means that all its components are of normal size, shape, and function correctly. Violations in any of hip components lead to dysplasia.
The structure of a hip joint.
A normal hip joint has the following structure.
The femoral head is located in the acetabulum. It is fixed in its place by the round ligament and the joint capsule. All construction should be rigid in a fixed position.
This is how hip dysplasia looks like.
Signs of Hip Dysplasia in Babies.
Five main features characterize hip dysplasia in infants. Basing on these 5 signs, you can identify or suspect this pathology in your baby. Each symptom separately is not a clear evidence of dysplasia. However, if there are two or more symptoms, you should consult a specialist.
Here are the 5 signs of hip dysplasia in newborns.
- Asymmetric skin folds on hips.
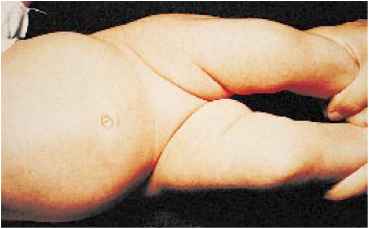
Asymmetry of skin folds is the most common and noticeable symptom of dysplasia in newborns, but not the most informative one, as asymmetry can be often observed in healthy children.
- Click symptom (or slippage)
Click symptom is the most informative sign of hip dysplasia in newborns. Sometimes a hip joint produces a characteristic clicking sound, which you can hear when you gently press the hip joint with your fingers. This symptom of infant dysplasia is the most characteristic indicator. However, it may disappear in 7−10 days after birth.
- Limited movement or pain
Limitation of motion or pain in the hips are also signs of dysplasia in babies. You can easily dissolve your baby’s legs bent at the knees if his hip joints are normal.
It’s almost impossible to do this if your baby has hip dysplasia because of the pain in the joint. This symptom may disappear within a week after birth, however, without treatment, it can appear again after the third month of a baby’s life.
- Different length of legs
If the knees of your baby are at different heights, you should immediately consult a doctor. This symptom is most valuable for diagnosing dysplasia in children under one year.
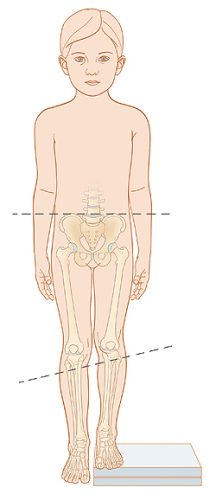
- External rotation of the hip
In early stages of dysplasia, external rotation is a rare symptom. External hip rotation means excessive foot turnout. Sometimes you can observe this symptom in healthy children with an excessive elasticity of ligaments.
Baby Hip Dysplasia Diagnostics
Each of the diagnostic methods for detecting hip dysplasia has its advantages and disadvantages. For the final diagnosis, it’s better to use more than one method.
Types of diagnostics:
- Inspection.
It is the simplest, but quite an informative method of initial diagnosis. During the inspection, it is possible to detect some signs of pathology that require further thorough examination.
- Ultrasound.
It is a harmless diagnostic method available from the first day of life. This study helps estimate the degree of acetabulum maturity, the condition of the femur head, its location in a calm state and in movement.
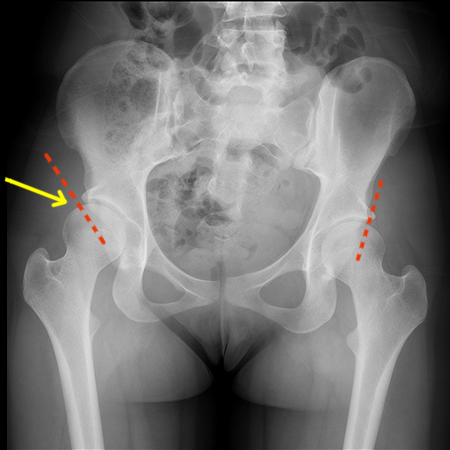
- X- ray
It is the most informative method of dysplasia diagnostics. However, it has two big cons:
- it is forbidden for babies under 7 months;
- it can’t show cartilage tissue, which prevails in infants.
Hip Dysplasia Prevention.
Preventive measures are usually limited to the elimination of predisposing factors. Dysplasia prevention at different times of a baby’s life is different.
- Prenatal development.
Eliminate all harmful factors in the first trimester of pregnancy — as it is the period when most organs and tissues are forming.
- Neonatal development (up to 1 year of life).
Medical inspection in critical periods is very useful for hip dysplasia prevention. The critical periods are:
- after birth
- at 1 month
- at 3 months
- at 6 months
- after your baby begins to walk
- at 1 year.
Avoid tight swaddling. Wide swaddling or lack of it is better for dysplasia prevention.
Possible Consequences of Hip Dysplasia.
Timely diagnosis usually plays a crucial role. Without treatment in the first year of life, a baby can develop some irreversible pathologies.
Dysplastic coxarthrosis arises from dysplasia in adulthood under the influence of critical factors such as pregnancy or decreased motor activity. It is characterized by acute onset with a limitation of motion, pain, and changes in gait. Dysplastic coxarthrosis often develops into ankyloses — a pathological installation of the joint in flexion.
Neoarthrosis — the formation of a new joint in the area of the pelvic bone. This is a kind of an organism adaptation to the congenital dislocation that has not been set and cured. Neoarthrosis allows to lead a normal life but is accompanied by thigh shortening and general dysfunction of the surrounding muscles and joints.
Trends in Dysplasia Treatment
First, you should consult an orthopedic surgeon and a rheumatologist. In the early stages of hip dysplasia, conservative treatment is enough. It means wide swaddling and using special orthopaedic appliances, as well as doing massage, exercise therapy, and physiotherapy. In more serious cases, surgery might be required to restore the joint. Arthroplasty is used at the advanced stages of hip dysplasia.
Modern medical diagnostic and treatment methods help detect and correct improper development of hip joints at the initial stage. Hip dysplasia treatment can be laborious and not very fast, but in most cases, it gives good results.




